Many real-world tasks involve multiple agents with partial observability and limited communication. While our previous works improved multiagent planning scalability, they assumed knowledge of a high-level domain model (e.g., probabilistic models over sensors and actions). Learning without knowledge of the underlying model is challenging in these settings due to local viewpoints of agents, which perceive the world as non-stationary due to concurrently-exploring teammates. Approaches that learn specialized policies for individual tasks face major problems when applied to the real world: not only do agents have to learn and store a distinct policy for each task, but in practice the identity of the task is often non-observable, making these algorithms inapplicable. This work formalizes and addresses the problem of multi-task multiagent reinforcement learning under partial observability.
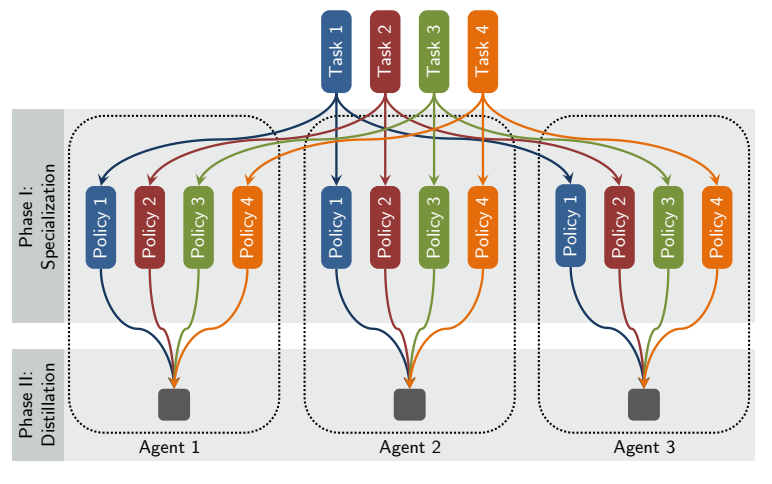
Our first contribution is a decentralized single-task learning approach that is robust to concurrent interactions of teammates. Our second contribution is an approach for distilling single-task policies into a unified policy that performs well across multiple related tasks, without explicit provision of task identity. Both the single-task and multi-task phases of the algorithm are demonstrated to achieve good performance on a set of multiagent domains. Our approach makes no assumptions about communication capabilities and is fully decentralized during both learning and execution. To our knowledge, this is the first formalization of decentralized multiagent multi-task learning under partial observability.