
Remote radiological source localization and mapping needed in first-response and disaster prevention scenarios in areas containing one or more radiation sources. UAVs provide ideal platforms for traversing arbitrary terrain when equipped with specialized, lightweight radiation sensors. Resolution of radiological sensing on a mobile platform is greatly improved when fused with pose estimates and 3D map information obtained through SLAM.
Single-agent aerial radiological mapping solutions such as the LAMP exist, and there is currently interest in determining whether their capabilities can be expanded in a coordinated multi-agent configuration. From a systems perspective, the following questions remain to be answered:
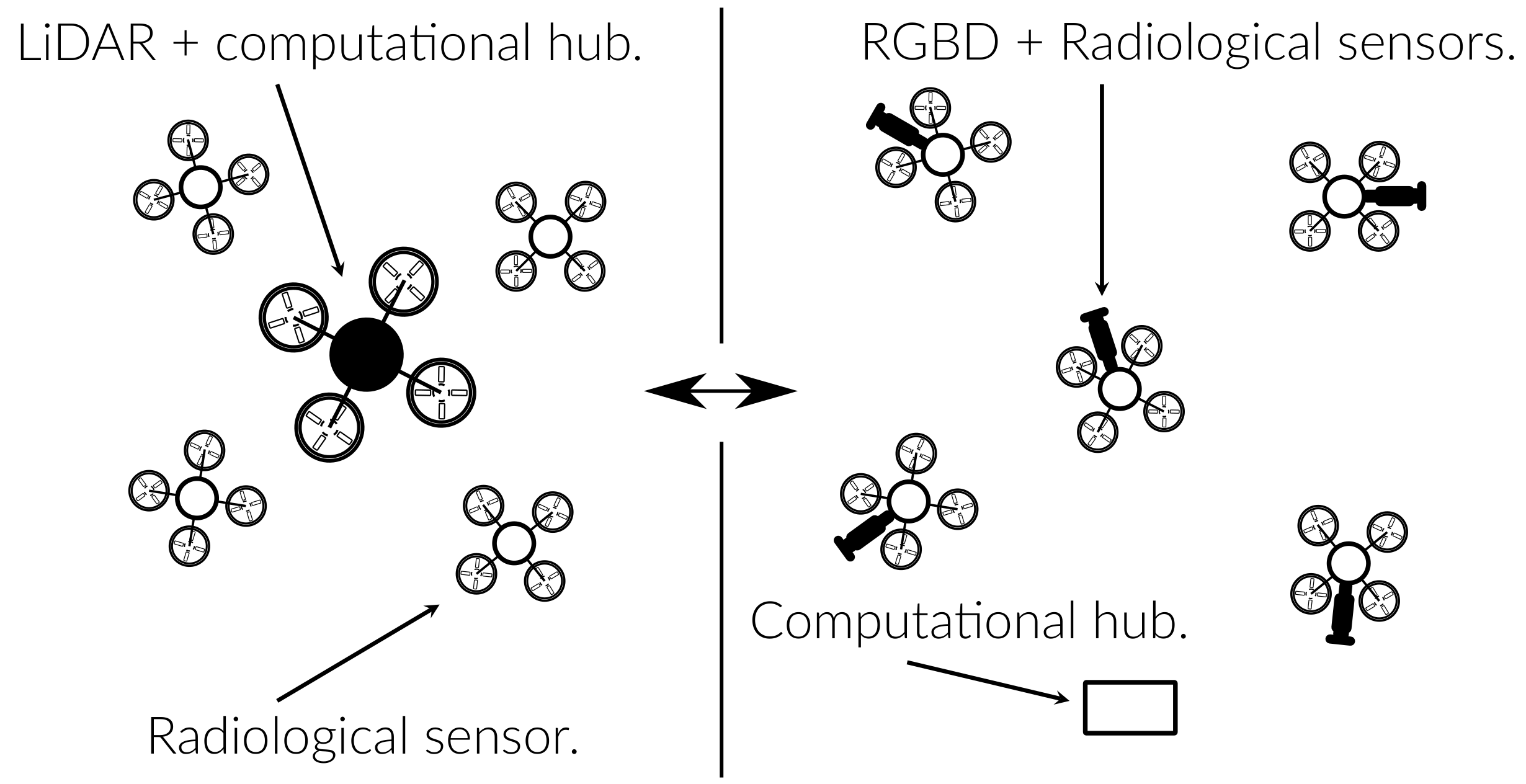
To determine what collaborative mapping architecture most efficiently enables multi-agent coordination in a radiological mapping setting, the following technical challenges must be addressed:
Approach: leverage current state-of-the-art in vision-based collaborative SLAM while adding novel contributions to resource-constrained, scalable map fusion and loop closure techniques.